3D Printing Prototypes: Driving Business Benefits
Navigation
- 3D Printing Prototypes
- Benefits of 3D Printing Prototypes for Businesses
- How to Implement 3D Printing in Your Business
- The Bottom Line
3D printing, a technology that creates three-dimensional objects from digital models, has evolved significantly since its inception. In product development, prototypes play a crucial role in bringing an idea to life. This article focuses on how 3D printed prototypes are revolutionizing business operations and product development, offering a blend of speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
3D Printing Prototypes
A 3D printed prototype is a preliminary model created using 3D printing technology. This intricate process involves layer-by-layer construction of objects from a variety of materials like plastic, resin, or metal. Despite the sophistication of this technology, like any other process, it may sometimes require troubleshooting 3D printed prototypes due to encountering common issues, but luckily, there are ways to fix them. The shift from traditional prototyping methods, which often require extensive manual labor and machinery, to the more streamlined, digital approach of 3D printing highlights not only the efficiency but also the versatility of this modern technology in creating perfect prototypes.

Benefits of 3D Printing Prototypes for Businesses
Speeding Up Product Development
The advent of 3D printing has not just improved but completely revolutionized the prototyping process through its ability to dramatically cut down the time required to bring a concept from design to tangible form. What traditionally took several weeks in creating a prototype, involving multiple stages from design, mold creation, to manual assembly, has now, thanks to 3D printing, shrunk to a matter of days or even hours, depending on the complexity of the design. As such, an increasing number of industries are seeing the need for 3D printing services. This swift turnaround is priceless in today’s fast-paced market where being first can often mark the difference between leading an industry, or merely following. It allows businesses to rapidly iterate designs, test ideas more frequently, and, in the grand scheme of things, accelerate the overall product development cycle, therefore significantly shortening the path from concept to commercialization.
Cost Reduction
The shift to 3D printing prototypes offers clear cost advantages over traditional prototyping methods, mainly due to its efficiency in material usage and labor. Unlike conventional processes that often involve expensive machinery and labor-intensive techniques, 3D printing streamlines the creation of prototypes. It employs an additive manufacturing process, building objects layer by layer, which dramatically minimizes material waste. This approach contrasts sharply with methods like CNC machining, where a significant portion of the material is carved away and discarded.
Furthermore, the automation characteristic of 3D printing leads to significant reductions in labor and operational costs. Once a design is programmed, the 3D printer can operate with minimal human intervention, thus decreasing the workforce required for prototype development. Some businesses opt for utilizing the best online 3D printing services to further enhance this effectiveness. Additionally, the speed of 3D printing is a crucial factor in cost reduction. Prototypes that traditionally took weeks to produce can now be completed in a matter of hours or days, drastically cutting down the production time. This expedited process not only reduces labor costs but also accelerates the product development cycle, enhancing a business’s ability to quickly adapt to market changes and consumer demands. These factors collectively make 3D printing a highly cost-effective solution for businesses, especially for those seeking to maximize efficiency and minimize development costs
Enhanced Design Flexibility and Innovation
The capacity of 3D printing to create complex and intricate designs with ease is one of its most compelling features. Traditional prototyping methods are often constrained by the limitations of manual craftsmanship and machinery capabilities. In contrast, 3D printing enables the creation of designs with a level of complexity and detail that would be either impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve through conventional means. This opens up a new area of possibilities for design innovation, allowing designers to experiment with complex geometries and structures, which can lead to more efficient, effective, and aesthetically pleasing products. The freedom to innovate without the constraints of traditional manufacturing methods fosters a culture of creativity and experimentation.
Testing and Validation of Designs
Prototypes are not just about how a product looks; they are also crucial for testing how it functions. 3D printed prototypes are essential in this regard, as they allow for comprehensive functional testing and design validation. This is especially important in industries where form closely follows function, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Prototypes enable designers and engineers to test their products under real-world conditions, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the final product performs as intended. This step is crucial in maintaining quality and safety standards and in avoiding costly recalls or redesigns post-production.
Customization and Small Batch Production
In an era where customization and personalization are increasingly valued, 3D printing offers significant advantages. It allows businesses to tailor products to individual customer needs without the need for large-scale production runs. This is particularly advantageous for niche markets, where demand might be for small quantities of highly specialized products. The flexibility of 3D printing makes it an ideal choice for producing custom or limited edition items, prototypes for crowdfunding campaigns, or bespoke components for specialized machinery. This adaptability opens new market opportunities and allows businesses to cater to specific consumer preferences, giving them a competitive edge in the market.

How to Implement 3D Printing in Your Business
Assessing Business Needs and Goals: Before diving into 3D printing, it’s crucial to evaluate how this technology aligns with your business objectives. Determine which products or components could benefit most from 3D printed prototypes. Consider factors like design complexity, customization requirements, and production volume.
- Choosing the Right 3D Printing Technology: There are various 3D printing technologies available, each suited to different applications. For instance, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is commonly used for basic prototypes, while Stereolithography (SLA) is better for detailed models. Selecting the appropriate technology depends on the desired prototype quality, material properties, and budget constraints.
- Material Selection: The choice of material is equally important and varies based on the required prototype durability, flexibility, and thermal resistance. Common materials include PLA, ABS plastic, resin, and metal alloys. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each material is essential to achieving the desired outcome.
- Starting with Pilot Projects: For businesses new to 3D printing, it’s advisable to begin with small-scale pilot projects. These projects serve as a practical learning experience, allowing your team to familiarize themselves with the 3D printing process and identify potential challenges in design, printing, and post-processing.
- Training and Skill Development: Ensure your team has the necessary skills to operate 3D printers and design for additive manufacturing. This might involve training existing staff or hiring new talent with specialized expertise in 3D printing.
- Quality Control and Testing: Establish quality control processes to ensure prototypes meet required specifications. This includes rigorous testing of prototypes for functionality, durability, and accuracy.
- Evaluating Cost-effectiveness and ROI: Monitor the cost implications and return on investment of using 3D printing. This evaluation should consider not just the direct costs of printing but also the indirect benefits, such as reduced time-to-market and enhanced product quality.
- Scaling Up: Once the pilot projects demonstrate success and the team is comfortable with the technology, consider scaling up 3D printing capabilities. This might involve investing in more advanced printers, experimenting with new materials, or integrating 3D printing more deeply into the product development process.
- Staying Updated with Advancements: 3D printing technology is rapidly evolving. Keeping abreast of the latest advancements and industry trends will enable your business to continually improve its prototyping processes and maintain a competitive edge.
- Partnering with Experts: Collaborating with 3D printing experts or service providers, such as QSYrapid, can provide valuable insights and access to advanced technologies without the need for significant upfront investment.
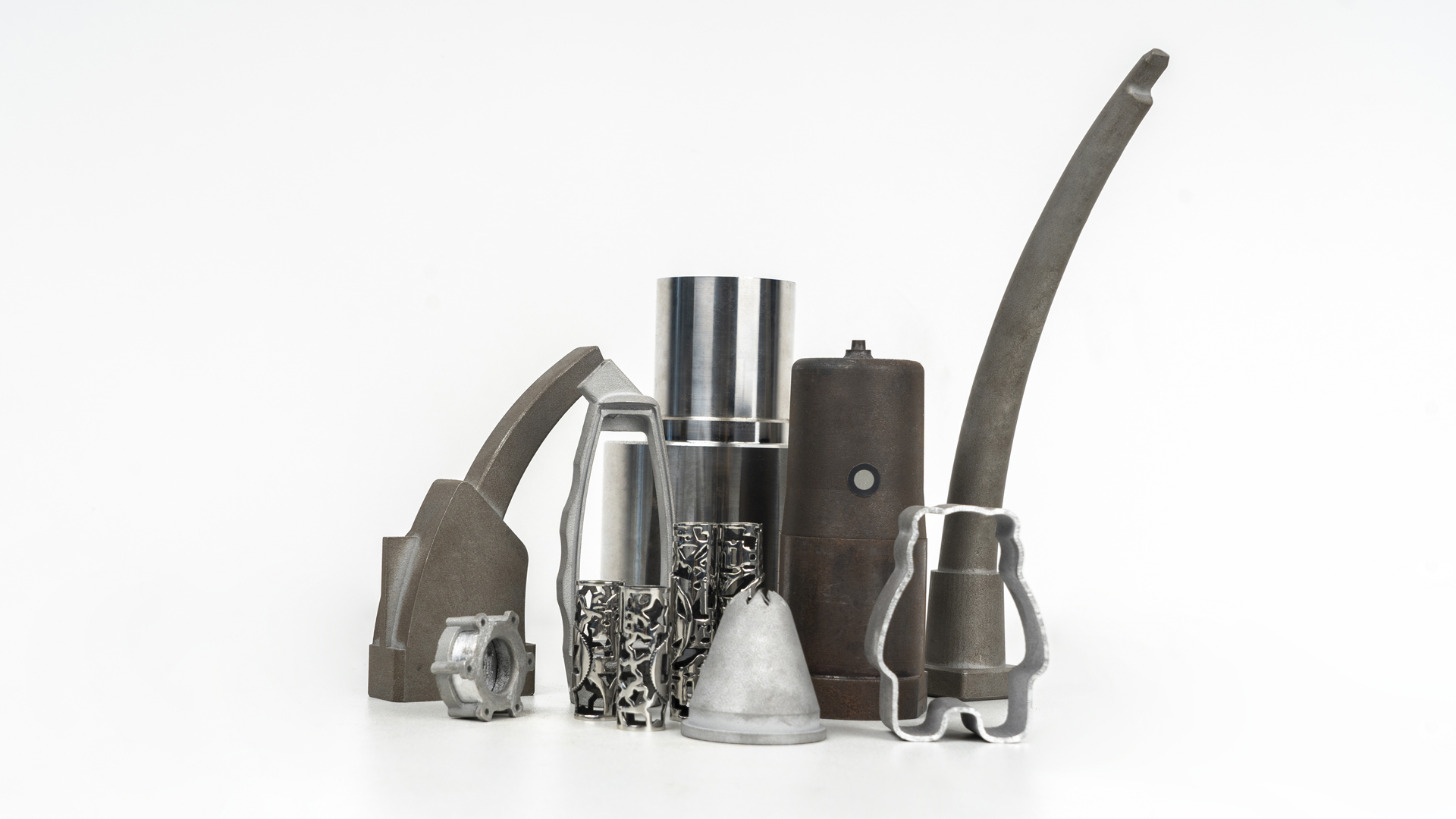

By methodically implementing these steps, businesses can effectively integrate 3D printing into their operations, reaping the benefits of enhanced innovation, reduced costs, and accelerated product development.
The Bottom Line
3D printed prototypes offer significant advantages for businesses, including speed, cost efficiency, design flexibility, and the ability to rapidly test and validate products. This technology is not just an iproveent but a transformative approach in the business world, reshaping how products are developed and brought to market.